Characteristics of Non-Programmed Decisions are distinctive attributes of choices made in unique and unpredictable situations, where established procedures or guidelines do not exist. For instance, a company's management deciding on a new product launch in a rapidly evolving market.
Understanding these characteristics is crucial for effective decision-making in dynamic environments. They guide leaders to adapt, innovate, and exploit opportunities while mitigating risks. Historically, the concept emerged from Herbert Simon's work in the 1950s, where he proposed that organizations need to make choices beyond routine operations.
This article explores the key characteristics of non-programmed decisions, including their complexity, lack of structured information, high stakes, and implications for organizational performance.
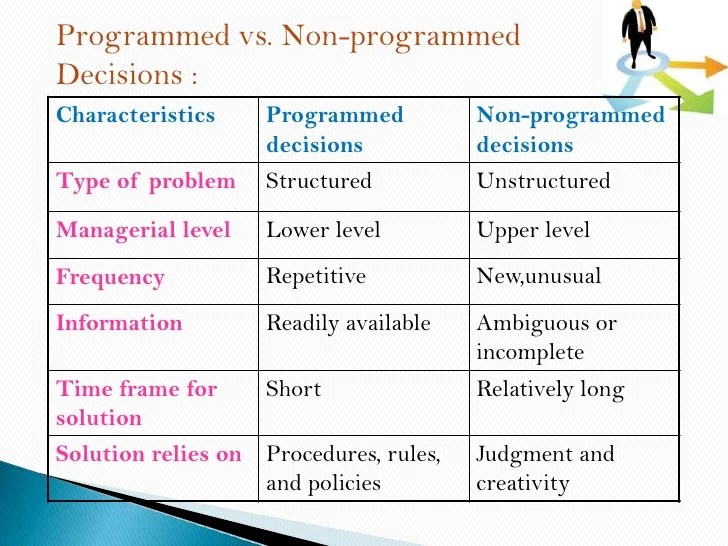
Characteristics Of Non-Programmed Decisions
Understanding the characteristics of non-programmed decisions is crucial for effective decision-making in uncertain and complex environments. These decisions involve unique challenges that require a nuanced approach.
- Complexity: High degree of uncertainty and multiple factors to consider.
- Lack of structure: No clear procedures or guidelines to follow.
- High stakes: Significant consequences for the organization.
- Subjectivity: Influenced by individual judgment and values.
- Non-routine: Occur infrequently and require customized solutions.
- Time-consuming: Demand extensive analysis and deliberation.
- Involve multiple stakeholders: Require input and collaboration from various parties.
- Strategic impact: Can shape the long-term direction and performance of the organization.
These characteristics highlight the challenges and opportunities associated with non-programmed decisions. By considering these aspects, decision-makers can navigate complex situations, foster innovation, and drive organizational success.
Complexity
Complexity is an inherent characteristic of non-programmed decisions. It arises from the uncertain and multifaceted nature of these decisions, where there is no clear path to follow. Unlike programmed decisions, which can be guided by established rules and procedures, non-programmed decisions require a more nuanced approach, as they often involve a multitude of interconnected factors.
For instance, consider the decision of a company to enter a new market. This decision is non-programmed because it involves a high degree of uncertainty and multiple factors to consider, such as market demand, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and potential risks. To make an informed decision, the company must analyze a vast amount of information, weigh the potential risks and rewards, and consider the long-term implications for the organization.
Understanding the complexity of non-programmed decisions is crucial for effective decision-making. It allows decision-makers to appreciate the challenges involved and to approach these decisions with the necessary level of care and deliberation. By considering the multitude of factors involved and the potential consequences of each decision, organizations can increase their chances of making sound choices that drive success.
In summary, complexity is a defining characteristic of non-programmed decisions. It highlights the uncertain and multifaceted nature of these decisions, requiring a thoughtful and analytical approach. Recognizing and addressing the complexity involved is essential for organizations to make well-informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives.
Lack of structure
In the realm of non-programmed decisions, the absence of clear procedures and guidelines is a defining characteristic. It distinguishes these decisions from programmed decisions, which can be guided by established rules and routines. This lack of structure presents unique challenges and opportunities for decision-makers.
- Unpredictability: Non-programmed decisions often arise in response to unforeseen events or changes in the environment. Without clear guidelines, decision-makers must rely on their judgment and creativity to navigate these uncharted territories.
- Adaptability: The lack of structure allows organizations to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. By not being bound by rigid procedures, decision-makers can explore innovative solutions and respond flexibly to emerging challenges.
- Trial and error: In the absence of clear guidelines, decision-makers may need to adopt a trial-and-error approach. This iterative process involves experimenting with different options and learning from the outcomes, allowing for continuous improvement.
- Subjectivity: Non-programmed decisions are often influenced by individual judgment and values. This subjectivity can lead to diverse perspectives and creative solutions but also poses challenges in reaching consensus and ensuring consistency.
The lack of structure in non-programmed decisions highlights the importance of critical thinking, flexibility, and open-mindedness. It requires decision-makers to embrace uncertainty, seek out diverse perspectives, and be willing to learn from their experiences. By understanding the challenges and opportunities presented by this characteristic, organizations can enhance their decision-making capabilities and thrive in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
High stakes
Non-programmed decisions are often characterized by high stakes, meaning they have significant consequences for the organization. This characteristic is intertwined with the other defining features of non-programmed decisions, creating a complex and challenging decision-making environment.
The high stakes involved in non-programmed decisions stem from the fact that these decisions are often made in situations of uncertainty and complexity. Without clear guidelines or procedures to follow, decision-makers must rely on their judgment and intuition, increasing the potential for significant consequences. These decisions can impact the organization's financial performance, reputation, and long-term success.
A real-life example of high stakes in non-programmed decisions is the decision of a company to launch a new product. This decision involves a high degree of uncertainty and risk, as the company must invest significant resources and effort with no guarantee of success. The consequences of a failed product launch can be severe, including financial losses, damage to reputation, and missed opportunities.
Understanding the connection between high stakes and non-programmed decisions is crucial for organizations. It highlights the need for careful consideration, thorough analysis, and effective risk management strategies. By recognizing the potential consequences of non-programmed decisions, organizations can make informed choices that align with their long-term goals and mitigate potential risks.
Subjectivity
Subjectivity is a defining characteristic of non-programmed decisions, as these decisions are often influenced by individual judgment and values. This characteristic plays a critical role in the decision-making process and has significant implications for organizational outcomes.
The subjectivity of non-programmed decisions arises from the lack of clear guidelines and procedures. In the absence of objective criteria, decision-makers must rely on their own judgment and values to assess the situation and make a choice. This can lead to diverse perspectives and creative solutions, as different individuals may perceive the same situation differently and prioritize different factors.
A real-life example of subjectivity in non-programmed decisions is the decision of a company to enter a new market. This decision involves a high degree of uncertainty and risk, and there is no clear path to success. The decision-makers must rely on their judgment and values to assess the potential risks and rewards, and to make a choice that they believe will benefit the organization.
Understanding the role of subjectivity in non-programmed decisions is crucial for organizations. It highlights the importance of fostering a culture of open-mindedness and collaboration, where diverse perspectives are valued and considered. By recognizing the subjective nature of these decisions, organizations can make more informed choices that align with their values and strategic objectives.
Non-routine
Non-routine decisions are a hallmark of complex organizational decision-making processes. Unlike programmed decisions that follow established procedures, non-routine decisions are unique, requiring customized solutions tailored to specific situations. This characteristic of non-programmed decisions has several key facets that influence organizational outcomes.
- Infrequent Occurrence: Non-routine decisions are not encountered regularly, making it difficult to develop standardized responses. This infrequency necessitates a flexible and adaptable approach to decision-making.
- Uniqueness: Non-routine decisions involve unique challenges and opportunities. Each situation presents a different set of variables, requiring decision-makers to carefully assess the context and tailor their solutions.
- Customized Solutions: Given their unique nature, non-routine decisions demand customized solutions. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, and decision-makers must consider the specific circumstances and constraints when developing a response.
- Innovation and Creativity: Non-routine decisions often require innovative and creative thinking. Decision-makers must be open to exploring new ideas and approaches to address complex challenges.
The non-routine nature of these decisions underscores the importance of effective problem-solving skills, adaptability, and a willingness to embrace creativity. By understanding the multifaceted nature of non-routine decisions, organizations can better prepare for and respond to the unique challenges they present.
Time-consuming
Within the realm of non-programmed decisions, their time-consuming nature stands as a prominent characteristic. These decisions often require extensive analysis and deliberation due to their complex and uncertain nature, posing unique challenges and implications for organizations.
- Information Gathering
Non-programmed decisions necessitate gathering vast amounts of information to fully understand the situation. This involves conducting thorough research, consulting experts, and analyzing relevant data.
- Stakeholder Involvement
Given the far-reaching impact of non-programmed decisions, involving key stakeholders in the analysis and deliberation process is essential. This ensures diverse perspectives and buy-in.
- Scenario Planning
To account for uncertainties, decision-makers must consider multiple potential scenarios and their implications. This involves developing contingency plans and assessing risk.
- Long-Term Considerations
Non-programmed decisions often have long-term consequences. Thus, decision-makers must carefully evaluate the potential impact on the organization's future.
The time-consuming nature of non-programmed decisions underscores the need for a strategic approach to decision-making. Organizations must allocate sufficient time and resources to ensure thorough analysis and deliberation. By recognizing and addressing the time-consuming aspect of these decisions, organizations can make well-informed choices that drive long-term success.
Involve multiple stakeholders
Within the context of non-programmed decisions, the involvement of multiple stakeholders is a critical characteristic. Unlike programmed decisions that may involve a limited number of decision-makers, non-programmed decisions often impact a wider range of stakeholders, necessitating their input and collaboration.
- Diverse Perspectives and Expertise
Involving multiple stakeholders brings diverse perspectives and expertise to the decision-making process. This can lead to more informed and comprehensive decisions that consider the interests of various parties.
- Increased Legitimacy and Acceptance
When stakeholders feel involved in the decision-making process, they are more likely to accept and support the final decision. This can increase the legitimacy and effectiveness of the decision.
- Organizational Learning and Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration among stakeholders can facilitate organizational learning and knowledge sharing. By working together, stakeholders can share their experiences, insights, and best practices.
- Improved Communication and Coordination
Involving multiple stakeholders can improve communication and coordination within the organization. By keeping stakeholders informed and engaged, organizations can avoid misunderstandings and ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.
The involvement of multiple stakeholders in non-programmed decisions is a key factor in effective decision-making. By considering the diverse perspectives and expertise of stakeholders, organizations can make well-informed decisions that are more likely to be accepted and supported. Furthermore, collaboration among stakeholders can foster organizational learning, improve communication, and enhance coordination, ultimately contributing to the success of the organization.
Strategic impact
Non-programmed decisions hold significant strategic implications, as they can profoundly shape the long-term direction and performance of an organization. The characteristics of non-programmed decisions, such as their complexity, lack of structure, high stakes, and involvement of multiple stakeholders, all contribute to their strategic impact.
The complexity and lack of structure inherent in non-programmed decisions necessitate a comprehensive understanding of the organization's strategic objectives and environment. This allows decision-makers to make choices that align with the organization's long-term goals and respond effectively to external changes. The high stakes associated with non-programmed decisions further emphasize the importance of considering their strategic implications, as the consequences of these decisions can have a lasting impact on the organization's success.
Involving multiple stakeholders in non-programmed decisions ensures that diverse perspectives and interests are taken into account. This collaborative approach allows organizations to make decisions that are more inclusive and responsive to the needs of various stakeholders, ultimately contributing to the organization's long-term performance.
Understanding the strategic impact of non-programmed decisions is crucial for organizations to make informed choices that align with their strategic objectives and ensure their long-term success. By considering the characteristics and implications of non-programmed decisions, organizations can develop effective decision-making processes that drive innovation, adaptability, and sustainable growth.
In conclusion, non-programmed decisions are characterized by their complexity, lack of structure, high stakes, subjectivity, non-routine nature, time-consuming analysis, involvement of multiple stakeholders, and strategic impact. These characteristics present unique challenges and opportunities for organizations, requiring a nuanced and deliberate approach to decision-making.
To effectively address non-programmed decisions, organizations should focus on understanding the complexity involved, fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability, and engaging in collaborative decision-making processes. By recognizing the interconnectedness of these characteristics, organizations can develop robust strategies to navigate uncertain and dynamic environments, driving long-term success and resilience.
Who is susan calman wife
Catherine reitman wiki bio age
Francesco gaetano caltagirone s net

ncG1vNJzZmifpaDBsL6NmqSsa16Ztqi105qjqJuVlru0vMCcnKxmk6S6cK%2FHmqmam6Sav6q%2F06KarGWfm3qvu81mp6unl6eurrnEnWSdnZOewKq7zaxloaydoQ%3D%3D